Electron. J. Diff. Equ.,
Vol. 2012 (2012), No. 89, pp. 1-19.
Local and global existence for the Lagrangian Averaged Navier-Stokes
equations in Besov spaces
Nathan Pennington
Abstract:
Through the use of a non-standard Leibntiz rule estimate, we prove the
existence of unique short time solutions to the incompressible,
iso\-tropic Lagrangian Averaged Navier-Stokes equation with initial
data in the Besov space
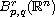 ,
,
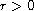 ,
for
,
for
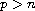 and
and
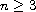 .
When
.
When
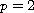 ,
we obtain unique local
solutions with initial data in the Besov space
,
we obtain unique local
solutions with initial data in the Besov space
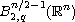 ,
again with
,
again with
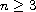 ,
which recovers the optimal regularity available
by these methods for the Navier-Stokes equation. Also, when
,
which recovers the optimal regularity available
by these methods for the Navier-Stokes equation. Also, when
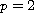 and
and
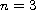 ,
the local solution can be extended to a global solution for all
,
the local solution can be extended to a global solution for all
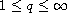 .
For
.
For
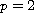 and
and
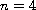 ,
the local solution can be extended
to a global solution for
,
the local solution can be extended
to a global solution for
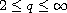 .
Since
.
Since
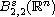 can be identified with the Sobolev space
can be identified with the Sobolev space
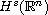 , this improves previous Sobolev space results,
which only held for initial data in
, this improves previous Sobolev space results,
which only held for initial data in
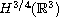 .
.
Submitted February 22, 2012. Published June 5, 2012.
Math Subject Classifications: 76D05, 35A02, 35K58.
Key Words: Navier-Stokes; Lagrangian averaging; global existence;
Besov spaces.
Show me the PDF file (308 KB),
TEX file for this article.
 |
Nathan Pennington
Department of Mathematics
Kansas State University
138 Cardwell Hall
Manhattan, KS 66506, USA
email: npenning@math.ksu.edu
|
|---|
Return to the EJDE web page
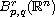 ,
,
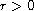 ,
for
,
for
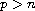 and
and
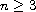 .
When
.
When
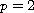 ,
we obtain unique local
solutions with initial data in the Besov space
,
we obtain unique local
solutions with initial data in the Besov space
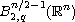 ,
again with
,
again with
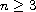 ,
which recovers the optimal regularity available
by these methods for the Navier-Stokes equation. Also, when
,
which recovers the optimal regularity available
by these methods for the Navier-Stokes equation. Also, when
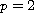 and
and
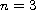 ,
the local solution can be extended to a global solution for all
,
the local solution can be extended to a global solution for all
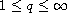 .
For
.
For
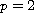 and
and
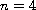 ,
the local solution can be extended
to a global solution for
,
the local solution can be extended
to a global solution for
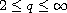 .
Since
.
Since
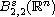 can be identified with the Sobolev space
can be identified with the Sobolev space
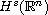 , this improves previous Sobolev space results,
which only held for initial data in
, this improves previous Sobolev space results,
which only held for initial data in
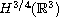 .
.
